
Overview: Menu Costs
| Type | Business Cost |
| Definition | The cost of changing your prices. |
| Examples | Advertising and promotion of new prices. ... |
| Related Concepts | Sticky Prices |
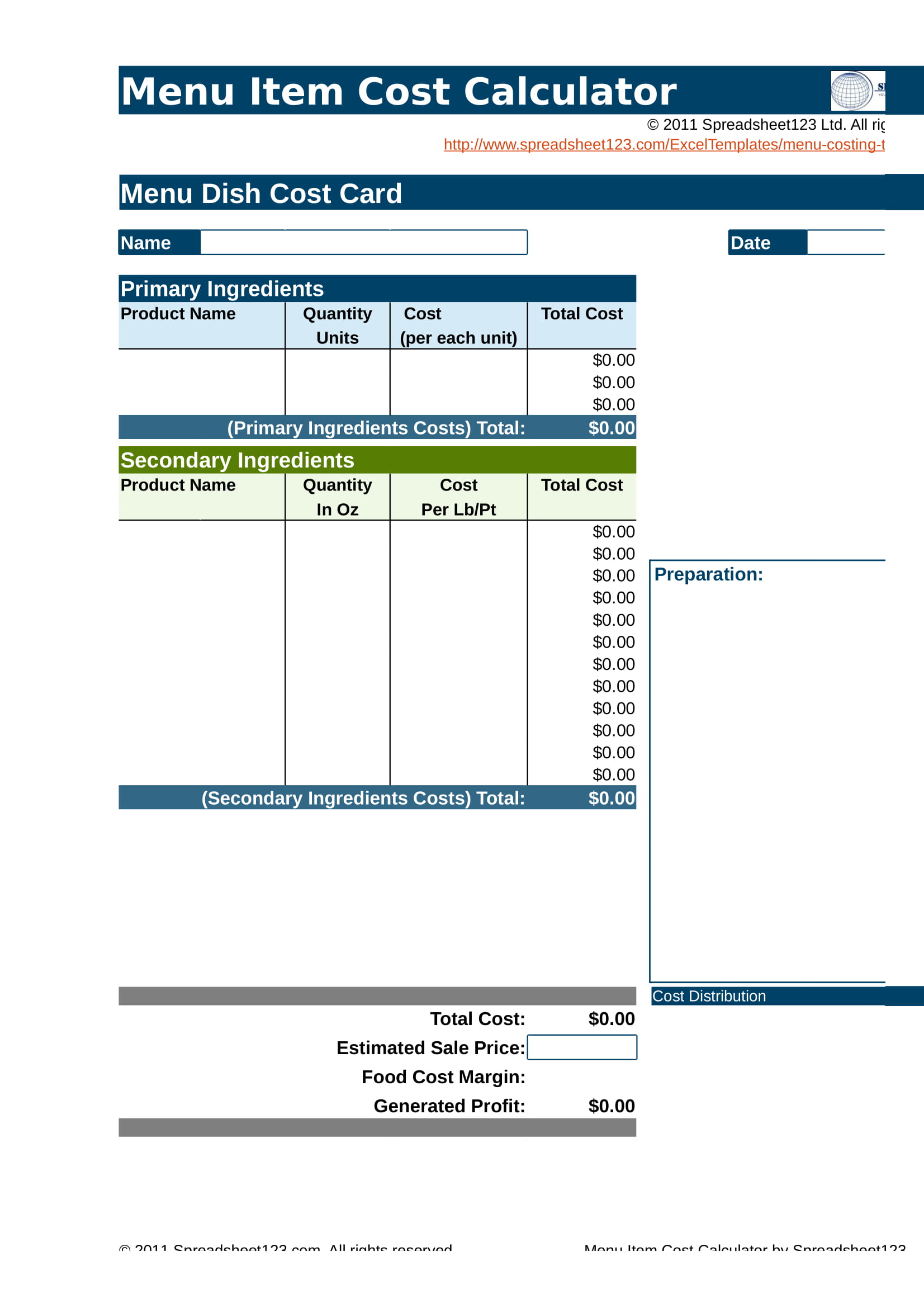
How to calculate food costs and price your restaurant menu?
- Choose an item on your menu.
- Insert the price of the item into the equation. Gross Profit Margin = (Menu Price – Raw Cost)/Menu Price
- Example: Say your menu price for a chicken Caesar salad is $14.50 and your raw food cost if $4. ($14.50 - $4)/$14.50 = 72% Gross Profit Margin. ...
How do you calculate meal cost?
Food cost calculations – how to calculate food cost per meal. In this case, take the cost of the food and divide it by the percentage food cost you wish to achieve, multiply by 100 to find the selling price and add the VAT. Example: To achieve food cost of 15%: Calculating Food Cost Percentage on a Monthly Basis – food cost formula
How to better manage food costs and menu pricing?
Tips to optimize food cost percentage
- Review your menu pricing strategy Menu pricing is key to ensuring your restaurant generates good revenues. ...
- Shop around for suppliers As much as it is important to get your pricing right, it is also important to reduce your costs whenever you can as this will ...
- Inventory management
How to set menu prices?
To estimate the actual cost, consider:
- Price per raw item - divide the total cost of a lot (delivery included) by the number of unprepared items.
- Prep time and approximate cost - estimate the time it takes your prep team to get the item ready to cook or serve. ...
- Cook time and approximate cost - estimate the time it takes to cook the item. ...

How do you price things on a menu?
Use the following equation: Price = Raw Food Cost of Item / Ideal Food Cost Percentage. You can slightly alter the price to make it a rounder or cleaner number. In the example below, you could change it to a number such as $14.50. Example: Say your ideal food cost percentage is 28%, and your raw food cost is $4.
What are menu costs quizlet?
Menu costs are the costs incurred by firms (businesses) when they have to change their prices. Most firms change their prices infrequently because of the costs of changing those prices. Things like: Changing the physical tags on the products.
Why do menu costs arise?
Menu costs are the result of a theoretical restaurant having to reprint menus because inflation is forcing the restaurant to change its prices. This means the restaurant will incur extra costs simply because of inflation.
What are menu costs in economics?
Menu costs are the costs incurred by a business when it changes the prices it offers to its customers. A classic example is a restaurant that has to physically print new menus when it changes the prices of its dishes. The main takeaway from menu costs is that some prices are sticky.
What is the difference between shoe-leather costs and menu costs?
Shoe-leather costs are the increased costs of transactions caused by inflation. Menu cost is the real cost of changing a listed price. Unit-of-account costs arise from the way inflation makes money a less reliable unit of measurement.
Which of the following correctly explains menu costs?
Which of the following correctly explains menu costs? The real costs associated with changing listed prices of goods and services.
How does inflation affect menu costs?
Menu costs This is the cost of changing price lists. When inflation is high, prices need frequently changing which incurs a cost. However, modern technology has helped to reduce this cost.
How do you calculate food cost per serving?
Calculating Actual Food Cost Percentage Per Dish FormulaCalculate what it costs for you to make a dish (a.k.a. Total Cost of Dish). ... Find out Price of Dish to Customer. ... Divide Total Cost of Dish Per Serving by Price of Dish to Customer. ... Multiply your answer by 100 to find out your Food Cost Percentage Per Dish.
What is menu cost?
Menu costs in economics refers to the cost to a commercial enterprise resulting from a price change. The term originates from the catering business – when a restaurant changes its prices, it has to design and print new menus – this costs money. Economists use ‘menu costs’ when talking about the costs of changing nominal prices in general.
When do economists use "menu costs"?
Economists use ‘menu costs’ when talking about the costs of changing nominal prices in general. Every time a firm raises or cuts the prices it charges, it faces a substantial outlay.
Why are businesses hesitant to alter their prices every time the supply and demand balance shifts?
Businesses are generally hesitant to alter their prices every time the supply-and-demand balance shifts because of the menu costs. When prices remain the same, despite a change in the supply-demand balance, we have sticky prices.
What happens if prices go up?
If prices keep going up everywhere, you will eventually have to raise yours too, which means paying money for people to design new catalogs, printing them, and hiring experts to determine what the new prices should be.
What is menu pricing?
Menu pricing is the engine behind your company's success, as sales are your restaurant's sole source of revenue. Pricing for food directly impacts your ability to fund essential aspects of your business, including equipment, utilities, labor, ingredients, and more. When creating or updating your menu, follow our tips below to effectively price your menu for maximal profits.
What should restaurant menu prices reflect?
In general, your restaurant menu prices should reflect your type of restaurant and your target demographic. In this way, your prices are cohesive with your brand, formality level, and food. Guests will appreciate if your price matches the value of your specific restaurant, and they will also be more likely to return.
What is gross profit?
Gross profit is an essential part of the equation that determines your net profit, otherwise known as your bottom line. The equation below shows you how to determine your net profit:
How to calculate gross profit margin?
If you already have your menu prices set, you can calculate the gross profit margin for each item on your menu with the same equation: Choose an item on your menu. Insert the price of the item into the equation.
What is a menu?
Your menu is your moneymaker, which means it plays a huge role in attracting guests to eat at your restaurant and consider it their usual haunts. Your aim with your menu is to get as many repeat customers as you can get. This means that your menu should contain items that are appetizing and affordable for the average consumer.
What is included in restaurant overhead?
In your calculations, you will include rent, labor, marketing, taxes, and other expenses. With this calculation, you will be able to determine the daily overhead expense to run your restaurant. The overhead cost that you require daily needs to be divided by the number of people you think you will serve each day.
What is the role of a menu in a restaurant?
Your menu is your moneymaker, which means it plays a huge role in attracting guests to eat at your restaurant and consider it their usual haunts.
What is included in ketchup?
This includes ketchup, mayonnaise, oil, garnishes, and seasonings. Always make sure that the portion size remains the same for all the dishes. Step 2. You need to calculate interest, return charges, delivery fees, and any other expenses related to a single ingredient such as the tomato.
Menu Costs and ‘Sticky Prices’
Menu Costs and E-Commerce
- As far as menu costs are concerned, the emergence of the Internet has been a godsend. As online transactions continue representing a greater proportion of total transactions across national economies and globally, companies are becoming less concerned about menu costs, and are adjusting their prices to respond to the conditions of the marketplace much more quickly, comp…
Do Menu Costs Cause Business Cycles?
- Economists have long been debating whether menu costs are large enough to cause business cycles. David Levy et al published the results of a study – ‘The Magnitude of Menu Costs: Direct Evidence from Large U. S. Supermarket Chains‘ – in the Quarterly Journal of Economics (1991).They demonstrated that menu costs are indeed big enough to cause business cycles. Le…