What is the formula for costing out a menu?
Raw food cost is similar to your cost of goods sold (COGS). Calculate your price. Use the following equation: Price = Raw Food Cost of Item / Ideal Food Cost Percentage. You can slightly alter the price to make it a rounder or cleaner number.
What are the four methods of menu pricing?
Types Of Restaurant Menu Pricing MethodsPricing by Portion Cost. A standard portion cost is the cost of serving one item or drink as per standard recipe. ... Pricing By Raw Food Cost Of Item. ... Pricing By Competition. ... Pricing By Demand Analysis.
What is the importance of menu costing?
Accurate pricing of menu items is vitally important for restaurants to succeed. If your prices are too high, your competitors will get your business. If your prices are too low, you'll miss out on profits.
How do you do costing for food?
How to Calculate Food Cost?Step 1: Break up each dish into its ingredients. ... Step 2: Calculate the cost of each dish. ... Step 3: Figure out your fixed cost per meal served. ... Step 4: Calculate what percentage of your menu price comes from food. ... Step 5: Determine target food-cost. ... Step 6: For established restaurants.
What is the best pricing method?
Value pricing is perhaps the most important pricing strategy of all. This takes into account how beneficial, high-quality, and important your customers believe your products or services to be.
What is food cost percentage?
Food cost percentage is calculated by taking the cost of goods sold and dividing that by the revenue or sales generated from that finished dish. The cost of goods sold is the amount of money you've spent on ingredients and inventory in a given period – we'll show you how to calculate that, too.
What is meant by Menu Costing?
Understanding Menu Costs Menu costs are the costs incurred by a business when it changes the prices it offers to its customers. A classic example is a restaurant that has to physically print new menus when it changes the prices of its dishes. The main takeaway from menu costs is that some prices are sticky.
What are the methods of costing?
Methods of Costing1] Job Costing. Many firms and businesses work on a job work basis. ... Browse more Topics under Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting. Origin and Evolution of Cost Accounting. ... 2] Batch Coting. ... 3] Process Costing. ... 4] Operating Costing. ... 5] Contract Costing.
What are food costing tools?
Food Costing Tools These are the tools and calculations that are important in deriving your food costs: Standard Recipe: Costing based on a standard recipe makes it easy to guide kitchen staff or food preparation. It also helps to compute food costs based on the servings that are needed. It is a basis for food costing.
How do you calculate food cost and selling price?
To calculate your food cost percentage, first add the value of your beginning inventory and your purchases, and subtract the value of your ending inventory from the total. Finally, divide the result into your total food sales.
How do you calculate portion cost?
Portion/serving size - How much of each ingredient goes into a dish you serve customers (e.g. 1 tablespoon of butter or 5 oz of beef.) Portion cost - The cost of the serving size for that ingredient, calculated using the following formula: Portion size x unit serving cost.
What is menu cost?
Menu costs are a type of transaction cost incurred by firms when they change their prices. Menu costs are one microeconomic explanation offered by New Keynesian economists for macroeconomic price-stickiness, which may cause an economy to fail to adjust to changing macroeconomic conditions.
What is menu cost theory?
Menu cost theory reflects the effect of a price change on a commercial enterprise. The classic example used to illustrate the theory is a restaurant that changes its prices must then bear the cost of printing new menus. Menu costs, then, are the costs to a firm of changing nominal prices in general. Every time a firm raises or cuts the prices it ...
Why are menu costs sticky?
That is, firms are hesitant to change their prices until there is a sufficient disparity between the firm's current price and the equilibrium market price to justify the expense of incurring the menu cost. For example, a restaurant should not change its prices until ...
What does it mean when menu costs are high?
In general, high menu costs mean that prices are generally not updated until they must be. For many goods, the adjustment is usually up. When input costs drop, the marketers of a product tend to pocket the extra margin until competition forces them to reprice.
Why are menu costs unavoidable?
Some menu costs are unavoidable because businesses must raise their prices at some point to keep up with inflation. However, a business can minimize menu costs by devising a pricing strategy that considers their unique value and branding compared to market competitors.
What is price stickiness?
Price-stickiness describes prices that do not adjust in response to macroeconomic changes. Prices that do not change with inflation can contribute to a recession. Companies can reduce menu costs by developing a wise pricing strategy so that fewer changes are necessary.
Why do restaurants have to raise their menu prices?
Menu costs usually are the result of inflation. For example, if the cost of food, rent, or wages goes up , a restaurant will have to raise its prices to pay for the extra cost and to make the same profit. When raising prices, there are additional costs, such as printing new menus, updating the website, etc. This means the restaurant will incur extra ...
Why Do Menu Costing?
When was the last time you updated your menu? Most experts agree that you need to update your menu seasonally, about four times every year. You should do this to account for trends, varying costs of your ingredients, and much more.
I Finished Menu Costing... Now What?
Now that we've learned what categories your menu items fall into, we'll take this knowledge one step further and come up with a plan to improve your menu and your bottom line. Prime recipes are what you need to focus your sales and advertising on.
What is menu pricing?
Menu pricing is the engine behind your company's success, as sales are your restaurant's sole source of revenue. Pricing for food directly impacts your ability to fund essential aspects of your business, including equipment, utilities, labor, ingredients, and more. When creating or updating your menu, follow our tips below to effectively price your menu for maximal profits.
What should restaurant menu prices reflect?
In general, your restaurant menu prices should reflect your type of restaurant and your target demographic. In this way, your prices are cohesive with your brand, formality level, and food. Guests will appreciate if your price matches the value of your specific restaurant, and they will also be more likely to return.
How to calculate gross profit margin?
If you already have your menu prices set, you can calculate the gross profit margin for each item on your menu with the same equation: Choose an item on your menu. Insert the price of the item into the equation.
What is gross profit?
Gross profit is an essential part of the equation that determines your net profit, otherwise known as your bottom line. The equation below shows you how to determine your net profit:
What is a menu?
Your menu is your moneymaker, which means it plays a huge role in attracting guests to eat at your restaurant and consider it their usual haunts. Your aim with your menu is to get as many repeat customers as you can get. This means that your menu should contain items that are appetizing and affordable for the average consumer.
What is included in restaurant overhead?
In your calculations, you will include rent, labor, marketing, taxes, and other expenses. With this calculation, you will be able to determine the daily overhead expense to run your restaurant. The overhead cost that you require daily needs to be divided by the number of people you think you will serve each day.
What is the role of a menu in a restaurant?
Your menu is your moneymaker, which means it plays a huge role in attracting guests to eat at your restaurant and consider it their usual haunts.
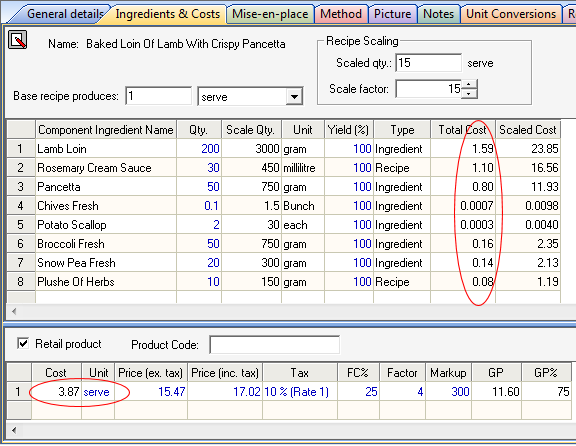
What is standard portion cost?
A standard portion cost is simply the cost of the ingredients (and sometimes labor) found in a standard recipe divided by the number of portions produced by the recipe. Standard portion costs change when food costs change, which means that standard portion costs should be computed and verified regularly, particularly in times of high inflation.
What is yield in cooking?
Yield in culinary terms refers to how much you will have of a finished or processed product. Professional recipes should always state a yield; for example, a tomato soup recipe may yield 4 gallons or 15 L, and a muffin recipe may yield 24 muffins. Yield can also refer to the amount of usable product after it has been processed (peeled, cooked, butchered, etc.) For example, you may be preparing a recipe for carrot soup. The recipe requires 2 lbs or 1 kg of carrots, which you purchase. However, once you have peeled them and removed the tops and tips, you may only have 1.6 lb or 800 grams of carrots left to use. In order to do accurate costing, yield testing must be carried out on all ingredients and recipes. When looking at yields, you must always consider the losses and waste involved in preparation and cooking. There is always a dollar value that is attached to vegetable peel, meat and fish trim, and packaging like brines and syrups. Any waste or loss has been paid for and is still money that has been spent. This cost must always be included in the menu price. Note: Sometimes, this “waste” can be used as a by-product. Bones from meat and fish can be turned into stocks. Trimmings from vegetables can be added to those stocks or if there is enough, made into soup. All products must be measured and yield tested before costing a menu. Ideally, every item on a menu should be yield tested before being processed. Most big establishments will have this information on file, and there are many books that can also be used as a reference for yields, such as The Book of Yields: Accuracy in Food Costing and Purchasing.
Do restaurants serve the same accompaniments?
Often, restaurants will serve the same accompaniments with several dishes. In order to make the costing of the entire plate easier, they may assign a “plate cost,” which would include the average cost of the standard starch and vegetable accompaniments.
Is there a dollar value to vegetable peel?
There is always a dollar value that is attached to vegetable peel, meat and fish trim, and packaging like brines and syrups. Any waste or loss has been paid for and is still money that has been spent. This cost must always be included in the menu price. Note: Sometimes, this “waste” can be used as a by-product.
Costing Your Food with Automatic Updates
Profitable restaurants usually keep food costs within 28 to 35 percent of gross income. This applies to the cost of food and waste, employee meals and theft. When you cost food, you analyze how much it costs to make each item on your menu. When you determine overall food cost percentages, you have to include waste.
Formulas for Pricing Foods
You can add all your expenses and subtract your inventory to determine total food costs, but pricing foods is a bit trickier. Once you’ve analyzed all the ingredient costs that go into a dish, you can divide the total by 0.35 to get the minimum cost that you need to charge. For example, a filet mignon might cost $6.00.
Portion Control and Alternative Serving Sizes
Portion control is critical because all your costs are based on exact quantities of raw ingredients. If your costs seem too low or too high for your customers, you can adjust prices by changing the sizes of the portions. Restaurants often offer optional smaller portions, but you should charge a higher percentage for a smaller serving.
Balancing Your Menu
It’s impossible to plan for every price fluctuation, so that’s why it’s important to balance expensive ingredients with lower cost items. Balancing your menu includes choosing foods that have stable prices to counter the prices that fluctuate frequently.
Pricing for Catering Jobs and Special Events
Pricing for catering and special events is more flexible, but it can be more challenging. Typically, your restaurant has certain fixed expenses, and the 28-to-35-percent food costs automatically make allowances for restaurant operating costs.
Costing & Pricing in Real World Conditions
After items have been priced, you have to pay attention to sales to see if the pricing works in real-world conditions. While your flexibility is limited, if a menu item won’t sell at a particular price you might have to take some kind of action, especially if the menu item is something special.
How much is gin tonic without VAT?
This means that the food costs for gin tonic without VAT would be 75 cents. Multiply the amount of expenses for one drink with four or five, and you will get your price for the drink. If you multiply drink expenses with 4 your earnings would be 75%, if you multiply costs with 5 your earnings will be 80%. In our example, gin tonic selling price ...
Do you have to be Einstein to calculate food costs?
The good news is that you don’t have to be Einstein to make those food costs calculations! But before you start to work read this text with easy to follow instructions as well as practical advice about costs calculation regarding food expenses and service in your restaurant or bar.
How to determine food costs for a new menu?
When determining food costs for a new menu, take your food costs, supplies and overhead into consideration. Every little thing counts. Know what your market can handle and price accordingly. Be sure to provide a menu that is worthy of its price, and you’re sure to encourage diners to return again and again.
How does service cost affect menu?
Service costs can raise or lower the prices of your menu depending on the type of restaurant. For example, you can charge less at a casual restaurant because you spend less on service. If your restaurant is fine dining, the prices go up. Don’t over-price here – make sure the price fits the quality of your service.
Why is it important to determine the cost of food?
Food costs are important to your bottom line. You want to determine your menu prices while implementing cost-controlling measures for added profitability. It’s vital to determine appropriate prices for your food because this is where your profits come from. (tweet this)
How to calculate food cost?
You want to take great care with your food cost fitness. Use your spreadsheet to calculate food costs and pay attention to the following: 1 Shop around for the best prices. 2 Brand management. Lesser known brands are often more cost effective. 3 Appropriate portion sizes. This cuts down on waste. 4 Meal composition. Use more of the less expensive items. 5 Dish size – make sure it’s appropriate to a smaller portion. 6 Use regular size serving utensils so you don’t serve too much. 7 Don’t give away too many freebies – think bread and butter.
What is overhead expense?
Overhead expenses are what it costs to run your restaurant such as your marketing strategy. Labor expenses are part of your indirect costs. For example, if you are cooking a labor intensive dish, you want to raise the price to accommodate the extra prep time and labor costs.
What is indirect cost in restaurant?
Indirect costs are the things you pay for that aren’t actually an ingredient. This is part of your restaurant that adds to the value and quality of your food – think table décor, ambiance, lighting, etc.
How much does it cost to buy 100 pounds of chicken?
For example, you buy 100 pounds of chicken at $1.50 per pound, so your purchase cost is $150. Say you use half a pound of chicken per portion $150/200 (half pound divided by 100), and you arrive at a cost of $.75 per portion. Do this for each part of the menu item.
